Mirboo North
Community Energy Hub


Mechanical Energy Storage
What is it?
Mechanical energy storage systems use kinetic and potential energy to generate on-demand electricity.
What are some examples?
Flywheels are a simple mechanical energy storage device that operate by conserving energy and momentum. A rotor is accelerated to maintain rotational energy. The system then slows when energy is drawn from it and speeds up when energy is stored in it. This allows for quick responses in energy production and make flywheels good for black out backups.
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is a storage system that is used with wind turbines. The turbines push compressed air into a holding tank underground. When there is a lack of wind and its resulting energy production, this compressed air can be released to power the generator and continue to produce electricity.
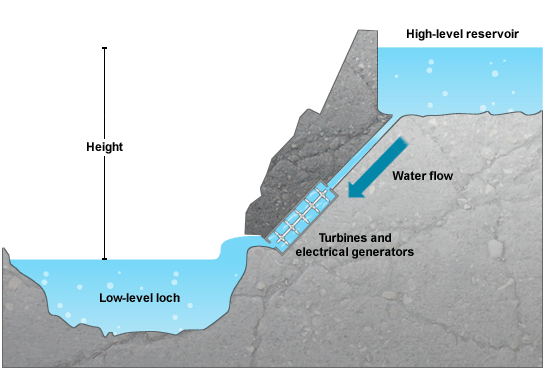
Pumped storage hydro (PSH) is a storage system that is combined with hydroelectricity systems. Water is pumped uphill into a holding tank by using free power from a renewable source or by using electricity from the grid during off-peak hours. Water can then be released from the tank and run through a turbine to generate electricty during peak hours.
Advantages:
-
flywheels can deliver energy in very short time increments
-
CAES provides long term storage
-
PSH provides long term storage
-
PSH can be intergrated into irrigation systems
Disadvantages:
-
flywheels are much less efficient than other methods
-
CAES systems are inefficient
-
PSH requires water turbines